Petri dishes are essential tools in microbiological experiments, providing a controlled environment for growing and studying microorganisms. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, outlining the step-by-step process of using and preparing a Petri dish for experiments. From properly setting up an agar plate to preparing the culture medium, we will explore the significance of Petri dishes in scientific research and provide expert tips for successful microbial cultivation.
Item No | Description | Spec.(mm) | Packing Info. | Qty./Case(pc) | Case Size(cm) |
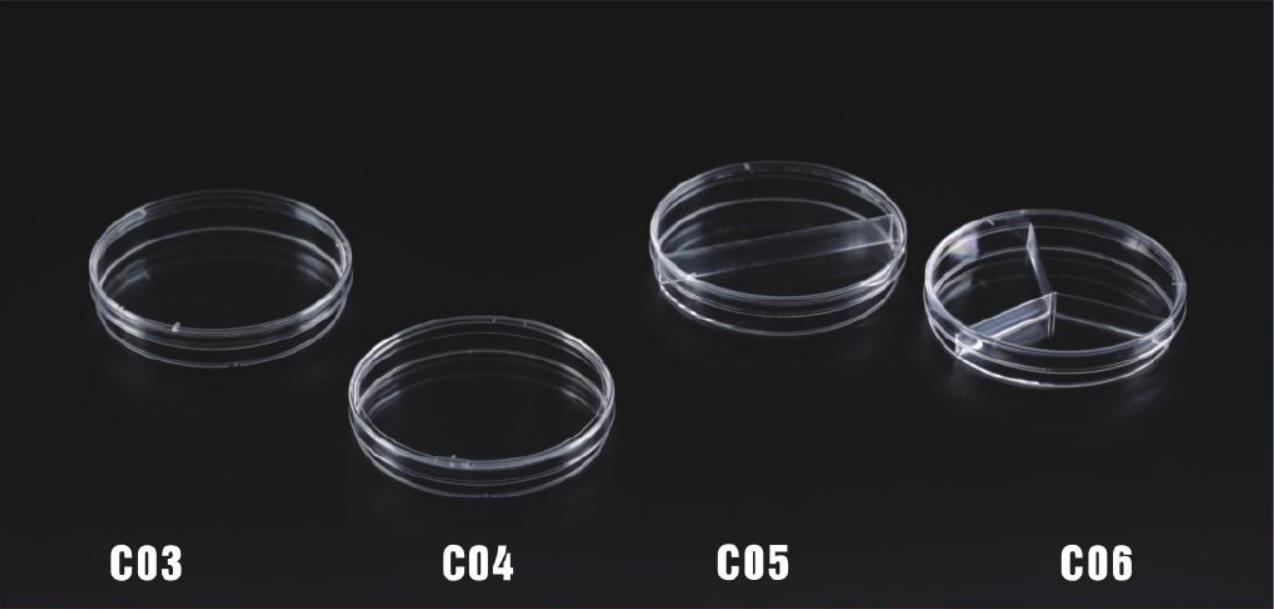
C03 | 90mm Petri Dish,Sterile,Size:¢92.5mm | ¢92.5*15 | 10pcs/bag X 50 | 500 | 49X49X34 |
C04 | 90mm Petri Dish,Sterile,Size:¢90mm | ¢90*15 | 10pcs/bag X 50 | 500 | 49X49X34 |
C05 | PETRI DISH 90mm, 2 compartments | ¢90*15 | 10pcs/bag X 50 | 500 | 49X49X34 |
C06 | PETRI DISH 90mm, 3 compartments | ¢90*15 | 10pcs/bag X 50 | 500 | 49X49X34 |
Petri dishes play a crucial role in microbiological experiments, providing a controlled environment for growing and studying microorganisms. Understanding how to properly use and prepare a Petri dish is essential for successful microbial cultivation and scientific research. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of setting up an agar plate and preparing the culture medium, ensuring accurate and reliable results in your experiments.
Gather the necessary materials: To start, ensure you have all the materials required for your experiment, including a Petri dish, agar powder, distilled water, and any necessary additives or supplements for the culture medium.
Sterilize the Petri dish: Before use, sterilize the Petri dish to eliminate any potential contaminants. This can be done by autoclaving or using a commercial sterilizing agent according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Prepare the agar mixture: Follow the specific protocol of your experiment to prepare the appropriate concentration of agar mixture. Dissolve the agar powder in distilled water and heat the mixture until it reaches a boiling point. Stir well to ensure proper dissolution.
Add any necessary supplements: Depending on your experiment, you may need to add specific supplements or additives to the agar mixture. This could include antibiotics, growth factors, or pH indicators. Follow the instructions provided for the precise amounts and proper mixing.
Pour the agar mixture into the Petri dish: Once the agar mixture has cooled down but is still in a liquid state, pour it into the sterilized Petri dish. Avoid creating air bubbles and ensure the medium evenly covers the bottom of the dish. Allow the agar to solidify completely.
Inoculate the Petri dish: Using sterile techniques, introduce microorganisms to the surface of the solidified agar. This can be done by streaking the microbes onto the agar using an inoculating loop or by placing a liquid culture directly onto the surface.
Incubate the Petri dish: Place the inoculated Petri dish in an incubator at the appropriate temperature required for the growth of your specific microorganisms. Follow the recommended incubation time for optimal microbial growth.
By following these steps, you can effectively use and prepare a Petri dish for microbiological experiments. The Petri dish provides a controlled environment for observing microbial growth, enabling scientists to study and analyze various aspects of microorganisms. Remember to maintain proper sterility throughout the process and adhere to safety protocols to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results.
In conclusion, Petri dishes are indispensable tools in microbiological experiments. By properly using and preparing a Petri dish, scientists and researchers can create controlled environments for the cultivation and study of microorganisms. Adhering to sterile techniques, preparing the agar medium accurately, and following appropriate incubation conditions are crucial for successful microbial growth and meaningful scientific discoveries.

Contact: Neo
Phone: 008615867460640
E-mail: Info@Hwtai.com
Whatsapp:008615867460640
Add: Building 2, Xinmao Qilu Science Technology Industrial Park, Tianqiao District, Jinan City, Shandong Province,China.
We chat
